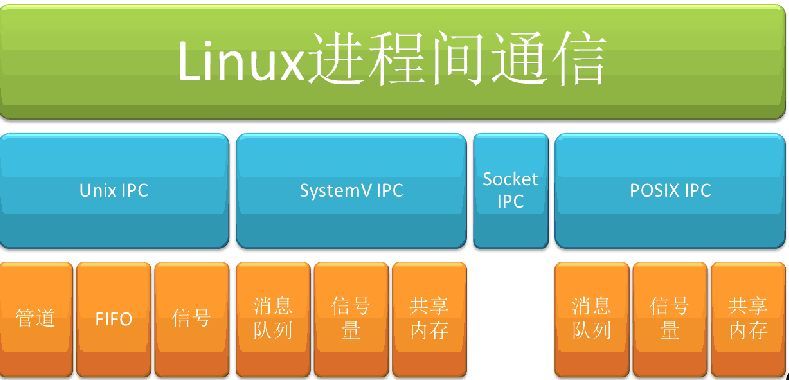
使用Linux shell脚本进行监控主要包括系统性能、资源使用情况和进程等方面的监控。
以下是几个不同场景的监控脚本示例。
![Linux shell脚本监控大全(Linux监控CPU、内存、磁盘、进程) 图片[1]-Linux shell脚本监控大全(Linux监控CPU、内存、磁盘、进程)-不念博客](https://www.bunian.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/u2792593542980670496fm253fmtautoapp138fJPEG-2.webp)
监控CPU使用率:
#!/bin/bashthreshold=80while true; docpu_usage=$(top -b -n1 | awk -v cpus=$(nproc) 'NR>7{s+=$9}END{print s/cpus}')if (( $(echo "$cpu_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); thenecho "Warning: CPU usage is over ${threshold}%"fisleep 10done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do cpu_usage=$(top -b -n1 | awk -v cpus=$(nproc) 'NR>7{s+=$9}END{print s/cpus}') if (( $(echo "$cpu_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); then echo "Warning: CPU usage is over ${threshold}%" fi sleep 10 done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do cpu_usage=$(top -b -n1 | awk -v cpus=$(nproc) 'NR>7{s+=$9}END{print s/cpus}') if (( $(echo "$cpu_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); then echo "Warning: CPU usage is over ${threshold}%" fi sleep 10 done
监控内存使用率:
#!/bin/bashthreshold=80while true; dototal_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $2}')used_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $3}')mem_usage=$(echo "scale=2; $used_mem*100/$total_mem" | bc)if (( $(echo "$mem_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); thenecho "Warning: Memory usage is over ${threshold}%"fisleep 10done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do total_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $2}') used_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $3}') mem_usage=$(echo "scale=2; $used_mem*100/$total_mem" | bc) if (( $(echo "$mem_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); then echo "Warning: Memory usage is over ${threshold}%" fi sleep 10 done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do total_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $2}') used_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $3}') mem_usage=$(echo "scale=2; $used_mem*100/$total_mem" | bc) if (( $(echo "$mem_usage > $threshold" | bc -l) )); then echo "Warning: Memory usage is over ${threshold}%" fi sleep 10 done
监控磁盘使用率:
#!/bin/bashthreshold=80while true; dopartitions=$(df -h | awk 'NR>1{print $1}')for partition in $partitions; dodisk_usage=$(df -h | grep $partition | awk '{print $5}' | sed 's/%//')if (( $disk_usage > $threshold )); thenecho "Warning: Disk usage for partition $partition is over ${threshold}%"fidonesleep 10done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do partitions=$(df -h | awk 'NR>1{print $1}') for partition in $partitions; do disk_usage=$(df -h | grep $partition | awk '{print $5}' | sed 's/%//') if (( $disk_usage > $threshold )); then echo "Warning: Disk usage for partition $partition is over ${threshold}%" fi done sleep 10 done#!/bin/bash threshold=80 while true; do partitions=$(df -h | awk 'NR>1{print $1}') for partition in $partitions; do disk_usage=$(df -h | grep $partition | awk '{print $5}' | sed 's/%//') if (( $disk_usage > $threshold )); then echo "Warning: Disk usage for partition $partition is over ${threshold}%" fi done sleep 10 done
监控特定进程:
#!/bin/bashprocess_name="your_process_name"interval=10while true; doif ! pgrep -x $process_name > /dev/null; thenecho "Warning: Process $process_name is not running"fisleep $intervaldone#!/bin/bash process_name="your_process_name" interval=10 while true; do if ! pgrep -x $process_name > /dev/null; then echo "Warning: Process $process_name is not running" fi sleep $interval done#!/bin/bash process_name="your_process_name" interval=10 while true; do if ! pgrep -x $process_name > /dev/null; then echo "Warning: Process $process_name is not running" fi sleep $interval done
注意:这些脚本只是简单的示例,在实际生产环境中,您可以根据您的实际需求进行修改和优化。
例如,您可以将警报写入日志文件或通过电子邮件发送,或者使用更高级的监控工具(如Nagios、Zabbix等)。
© 版权声明
本站文章由不念博客原创,未经允许严禁转载!
THE END