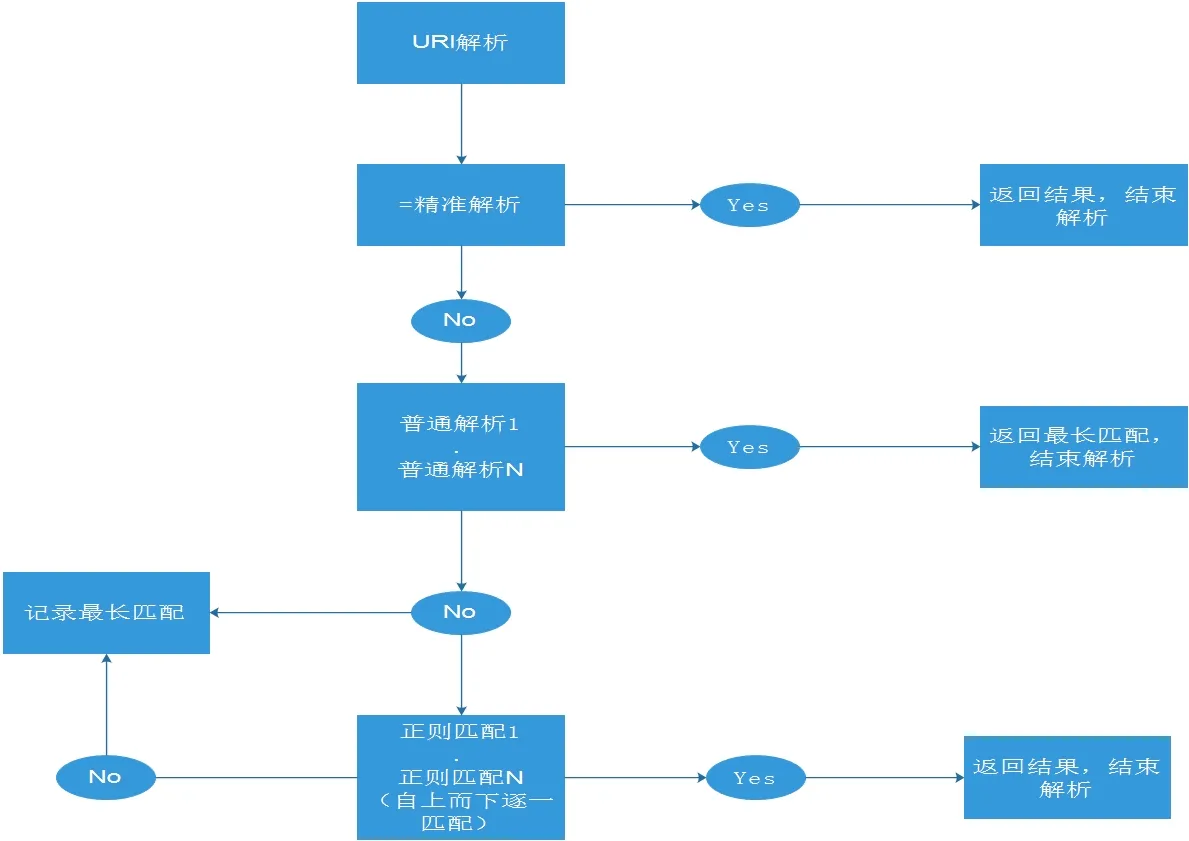
Location 基础知识:
概念:
我们可以通过配置Location指令块,来决定客户端发过来的请求URI如何处理。
语法:
Syntax: location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
location @name { ... }
Default: —
Context: server, locationlocation 配置可以有两种配置方法,可以在server指令块和location指令块配置。
1、修饰符 + uri(资源路径)
2、@ + name
修饰符:
= :精确匹配(必须全部相等)
~ :大小写敏感(正则表达式)
~* :忽略大小写(正则表达式),这里要注意忽略大小写的意思是请求的字符大小写都可以,
但是不会进行大小转换,请求的大小写对应的文件必须存在。
^~ :只需匹配uri部分
@ :内部服务跳转Location 配置实例:
1、=,精确匹配,一般是匹配某个具体文件。
location = /index.html {
[ configuration ]
}
# 则匹配到`https://www.bunian.cn/index.html`这种请求。 还有这种写法,精准匹配/,可以加快首页访问速度。
location = / {
root html;
index index.html;
}有一点需要注意,如果想变更根目录,比如把根目录设置为/usr/local/nginx/html/bunian,那么直接这么写可能会出问题,假如原根目录(html)没有index.html文件,会报404。
location = / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/bunian;
index index.html;
}
如果写成这样的话,即使bunian目录下有index.html,也会直接报错,报找不到文件。解释:
当我们访问www.bunian.cn/时,确实匹配到了这个location,
但是这个时候请求的前缀会变成/index.html,所以已经不再匹配这个localtion规则。
因为找不到其他匹配规则,
所以默认会去匹配根目录下(/usr/local/nginx/html)的文件,但是这时根目录下的index.html不存在,
所以报错404。同样的,如果bunian目录里面有其他的文件,我们通过这个localtion规则也是无法访问的, 因为它只匹配/,其他的url都不再是它匹配。
那么怎么解决这个问题呢?可以在加一个location。
location = / {
root html/bunian;
index index.html;
}
location / {
root html/bunian;
index index.html;
}
通过加这个location,凡是没有匹配到的资源会到/目录下去找
,根的目录重新定义了,所以可以实现这个需求。2、~,大小写敏感(正则表达式)
location ~ /BUNIAN/ {
[ configuration ]
}
#请求示例
#https://www.bunian.cn/BUNIAN/ [成功]
#https://www.bunian.cn/bunian/ [失败]3、~*,大小写忽略(正则表达式)
location ~* /LUTIXIA/ {
[ configuration ]
}
# 则会忽略 uri 部分的大小写
#https://www.bunian.cn/BUNIAN/ [成功] 可以成功匹配,但是目录中要BUNIAN文件
#https://www.bunian.cn/bunian/ [成功] 可以成功匹配,但是目录中要bunian文件4、^~,只匹配以 uri 开头,匹配成功以后,会停止搜索后面的正则表达式匹配
location ^~ /img/ {
[ configuration ]
}
#以 /img/ 开头的请求,都会匹配上
#https://www.bunian.cn/img/bunian.jpg [成功]
#https://www.bunian.cn/img/bunian.png [成功]5、匹配以gif、jpg、jpeg结尾的文件
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration ]
}
#https://www.bunian.cn/img/bunian.jpg [成功]如果配置了4,那么所有请求 /img/ 下的图片会被上面4处理,因为 ^~ 指令匹配到了,则不检查正则表达式。
6、@,nginx内部跳转
location /data/ {
error_page 404 @img_err;
}
location @img_err {
[ configuration ]
}
#以 /data/ 开头的请求,如果链接的状态为 404。则会匹配到 @img_err 这条规则上。同时有多个location时,优先级如下:
完整范例:
这里有一简短的localtion配置:
location /img/ {
echo " /img/";
}
location ~ /img/ {
echo "~ /img/";
}
location ~* /img/ {
echo "~* /img/";
}
location ^~ /img/ {
echo "^~ /img/";
}
location = /img/ {
echo "= /img/";
}如果客户端的请求是:
http://192.168.0.166/img/那么按照匹配规则顺序应该是这样的:
第一步:取出uri:/img/
第二步:去匹配localtion规则,查找有没有 = /img/的规则,有则停止匹配。
[root@www ~]# curl 192.168.0.166/img/= /img/第三步:将location = /img/规则注释,继续查找有没有 ^~ /img/的规则,
[root@www ~]# curl 192.168.0.166/img/^~ /img/第四步:将 location ^~ /img/注释,这是它会去查找有没有正则匹配规则。
location /img/ {
echo " /img/";
}
location ~ /img/ {
echo "~ /img/";
}
location ~* /img/ {
echo "~* /img/";
}
# location ^~ /img/ {
# echo "^~ /img/";
# }
# location = /img/ {
# echo "= /img/";
# }第五步:其他的都注释后,因为优先匹配规则都没有找到,最后匹配到 /img/规则。
[root@www ~]# curl 192.168.0.166/img/ /img/© 版权声明
本站文章由不念博客原创,未经允许严禁转载!
THE END